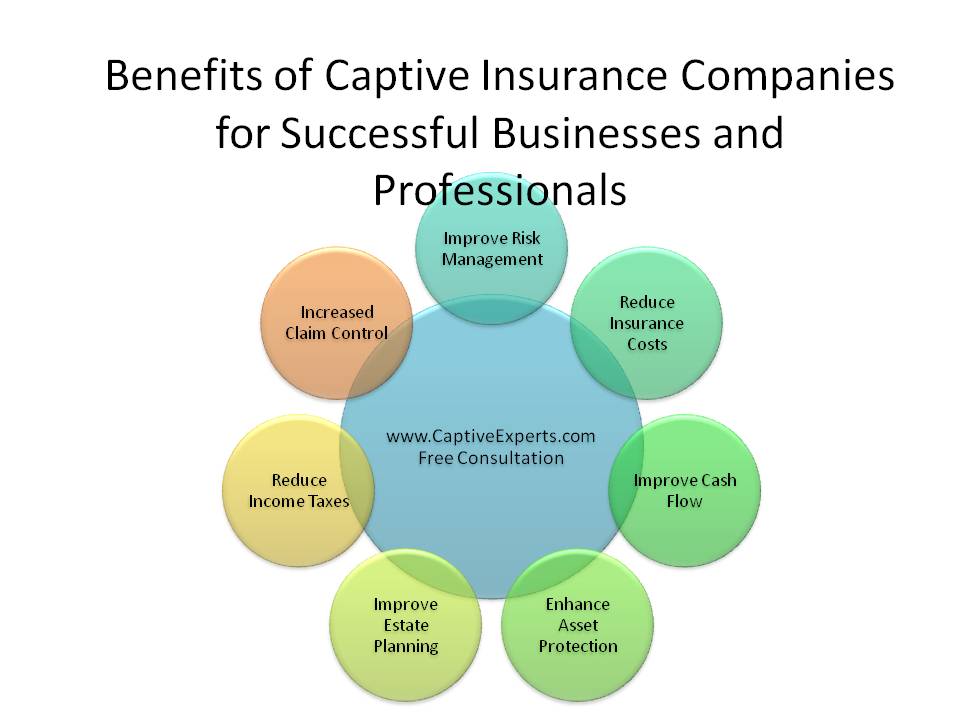
Effectively designed and managed captive insurance companies achieve these goals and objectives:
- Improve cash flow predictability and balances
- Retain control over risk assets (investment reserves accumulating to cover potential future losses)
- Improve risk coverage – customize insurance program to cover previously uncovered risks
- Reduce insurance expense and lower risk financing cost (retain profits previously earned by commercial insurance companies)
- Create new profit center (well designed captives should be very profitable and often can create new revenue streams)
- Minimize taxes
- Increase asset portfolio liquidity
- Avoid the volatility of the cyclical insurance market
- Tailor insurance policies and programs to your specific needs
- Improve risk management by controlling risk via improved claims management, underwriting flexibility and access to wholesale reinsurance markets
- Improve Claim Reserve Investment Management
- Capture Underwriting Profits (commercial insurance companies are generally very profitable as are most captives)
- Increase tax saving opportunities (insurance companies benefit from favorable accounting and tax rules)
- Expand wealth accumulation options (tax leveraged wealth accumulation possible)
- Protect assets (significant asset protection possible with the advanced ownership structures allowed today)
- Reduce asset transfer costs (improve estate tax planning)
Main Risks/Cons of Captives
Captive insurance companies are not a solution for every situation but they go a long way towards improving business risk management practices. The business risks of owning a licensed insurance company are many including:
- Can be expensive to form, capitalize and operate (unless you engage Captive Experts LLC)
- Poorly designing or operating your captive causing unexpected liabilities and costs
- Restrictions on captive investments (we have sophisticated methods to expand investment options)
- Exposure to regulatory sanctions and fines
- Failing to qualify for targeted tax incentives
- Unexpected windup costs and taxes