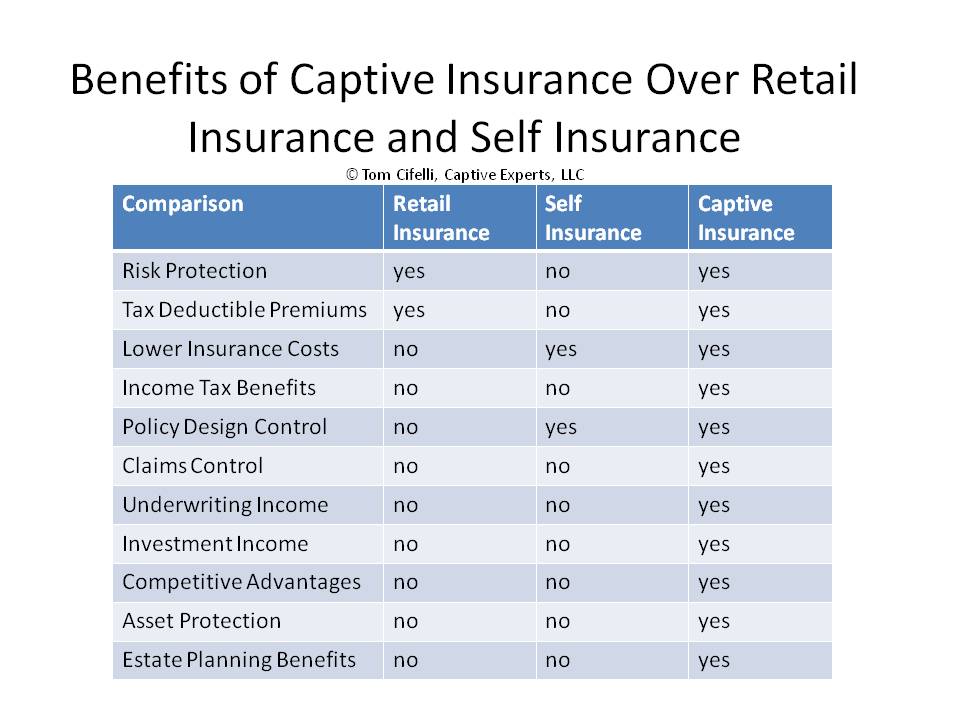
The main goals of most captive insurance companies used today are two-fold:
- to buy insurance from your own insurance company and deduct premiums to cover previously self insured risks – this allows using pre-tax dollars, verses after tax dollars, to build loss reserve assets, and
- to save $$$ on commercial insurance expenses (by internalizing underwriting profits and lowering costs previously paid commercial insurance companies).
Secondary benefits are many – see the chart below. To begin the analysis of how a captive can specifically benefit you, click here.
Captive insurance companies have been around for hundreds of years. Nearly every Fortune 500 company owns a captive. Thirty years ago there were 500 captives worldwide, all formed outside the US. Today there are nearly 7000 captives, with over half of the 2013 newly formed captives licensed by a US state and most of these newer captives part of a successful family owned business enterprise group.
Captives are part of the world known as “Alternative Risk Transfer (ART), also known as Alternative Risk Finance.” The ART industry is a response to commercial insurance programs that, either for regulatory or business reasons, do not respond quickly and efficiently to the ever changing risk environment of commercial and nonprofit enterprises. The main benefits of captives are customized insurance programs to better cover and finance risk exposures of concern, ability to lower commercial insurance expenses or internalize some of the profits being made by commercial insurance companies, protecting assets, improving claims control, accessing the wholesale insurance market known as reinsurance, reducing taxes to subsidize creation of loss reserve assets, and other benefits.
Captives are different from commercial insurance companies primarily because a captive has a restrictive insurance license – a captive cannot sell insurance to the general public. They are licensed and regulated specialized insurance companies that can sell custom insurance policies to companies affiliated with the captive’s owners, and in some cases to customers of those affiliated companies.
Some Widely Used Definitions of a Captive
A.M. Best’s Captive Directory uses this definition when deciding which insurance companies should be included in the “captive” section of its insurance rating directory:
“A captive is an insurance company that is wholly owned and controlled by its insureds; its primary purpose is to insure the risks of its owners; the primary beneficiaries of its underwriting profits are its insureds.”
Wikipedia defines captives as:
“Captive insurance companies are insurance companies established with the specific objective of financing risks emanating from their parent group or groups, but they sometimes also insure risks of the group’s customers as well. Using a captive insurer is a risk management technique by which a business forms its own insurance company subsidiary to finance its retained losses in a formal structure.”
Browse the many pages part of this About Captives section of our website to learn how captives can benefit your organization. To visit our sister site with articles, white papers and current information on captive hot topics, click here.
Political Trend Note
The global captive industry is trending toward a loss of design and program structure freedom. Regulators continue expanding regulations and examination scope and frequency; not because industry practices require heightened “police” action to protect the public, but rather symptomatic of a wider trend toward more government regulation of the private sector across most industries. In the US this is occurring by licensing domiciles and also by the IRS taxing authority which continues challenging captives, especially on risk shifting and risk distribution characteristics, in an effort to deny the benefits of special accounting and tax rules afforded insurance companies over general business organizations. These heightened regulatory requirements, adding costs, limitations and complexity to captive risk management design, ironically are increasing the need for advanced enterprise risk management and wealth protection strategies which captives are a strategically important part of.